
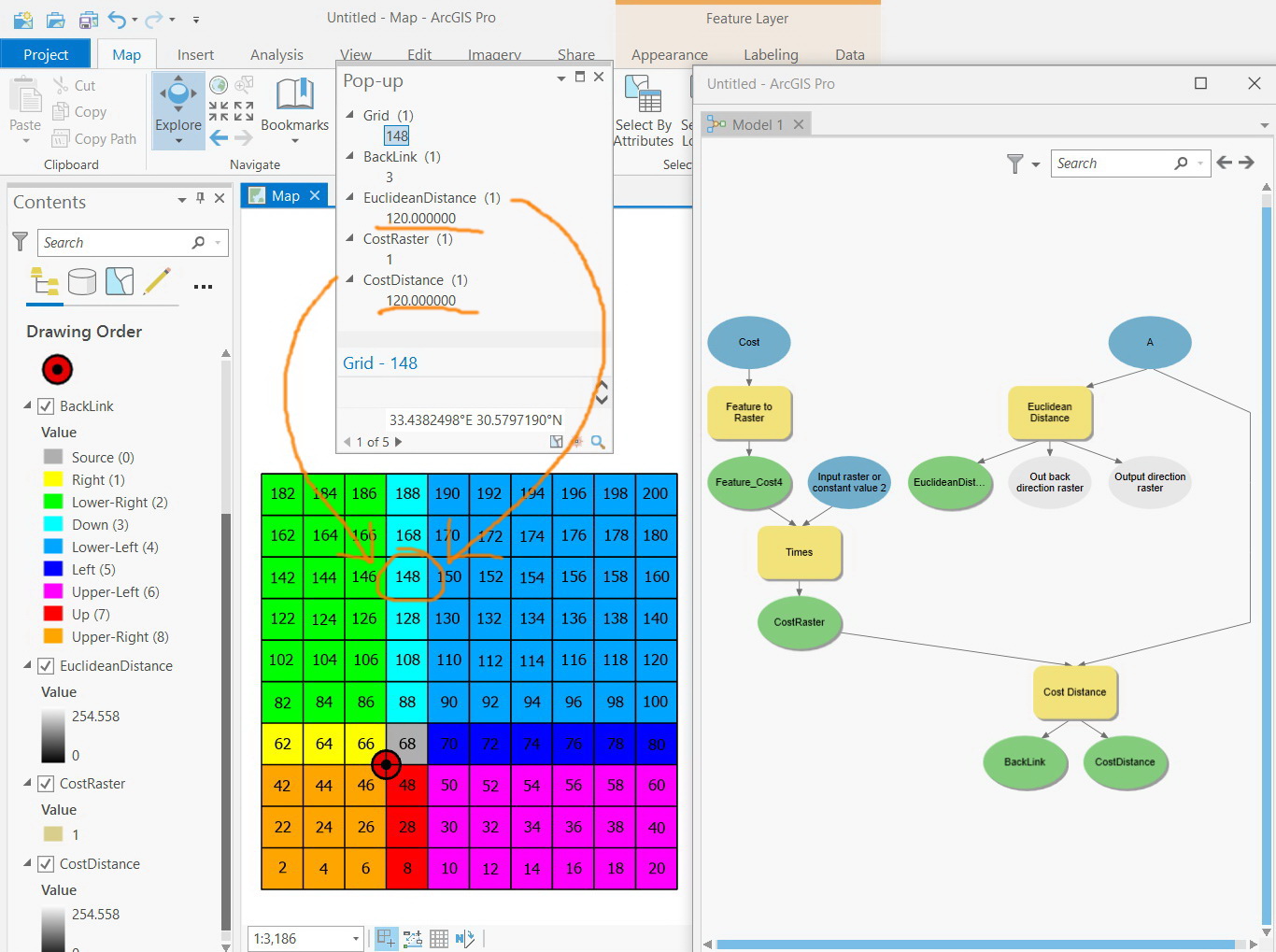
The output values for the Euclidean distance raster are floating-point distance values. The shortest distance to a source is determined, and if it is less than the specified maximum distance, the value is assigned to the cell location on the output raster. This calculation derives the true Euclidean distance, rather than the cell distance. Conceptually, the Euclidean algorithm works as follows: for each cell, the distance to each source cell is determined by calculating the hypotenuse with x_max and y_max as the other two legs of the triangle. True Euclidean distance is calculated in each of the distance tools. The Euclidean distance algorithmĮuclidean distance is calculated from the center of the source cell to the center of each of the surrounding cells. If the source is a feature, it will internally be transformed into a raster when you run the tool. If the source is a raster, it must contain only the values of the source cells, while other cells must be NoData. The source identifies the location of the objects of interest, such as wells, shopping malls, roads, and forest stands. Euclidean Allocation identifies the cells that are to be allocated to a source based on closest proximity.Įxample of usage: What is the closest town?.Euclidean Direction gives the direction from each cell to the closest source.Įxample of usage: What is the direction to the closest town?.Euclidean Distance gives the distance from each cell in the raster to the closest source.Įxample of usage: What is the distance to the closest town?.The Euclidean distance tools describe each cell's relationship to a source or a set of sources based on the straight-line distance.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
